Introduction
If you work in IT industry, you must heard somethings about software architecture. Moreover, software architecture are playing a more and more important role in the industry. In order to have a success in software development, we need to have a good software architecture. Software architecture captures early decisions about the high-level design, and allows reuse of design components between projects. However, the software architecture is not an easy concept. There are many things to learn to become an architect, the body of knowledge about software architecture is huge enough to fill hundreds of books. Let us have some basic ideas on software architecture here.
In short, Software architecture describes the structures of a computer system. A software architecture consist of software elements with their system modules or software components. The external visible properties typically represent services provided to other elements. The relationships of element usually describe how elements interact with others.
As an architect, you need to balance the different stakeholder benefit in order to have a “good" software architecture, remember that you cannot 100% fulfil of each stakeholder as resources is always limited and there are conflicts among the requirements.
Need for Architecture
Why architecture is needed in modern software? Three crucial changes in software engineering have led to us to aware the importance of architecture, they are Scale, Distribution and Security. During the past decade, the scale of IT systems extend much, there are many large system with hundreds of server and thousands of process running in the computer system. Moreover, the capability of scale up are now natural requirement of the computer system. On the other hand, the computer system is migration from mainframe to highly distributed system known as cloud. Finally, we have enhanced many security features in the computer system as the security nowadays is a major quality of a system.
The Goal of Architecture
With the three crucial changes of computer system, software architecture aim to resolve the issues of scalability, distribution and security. Furthermore, the software architecture also help to reduce project risks and capture quality-related decisions. On the other hand, software architecture can facilitate the design, implementation and deployment of the application. Software architecture focuses on quality-related requirements, instead of functionalities. The goals of software architecture often include the bridge of the abstract business ideas to a concrete computer system. Followings are common goal of software architecture:
- Improve quality of services(QoS) of the system such as scalability, portability and maintainability.
- Building a effective secure environment.
- Respond various changes
- Handling the complexity in a effective manner
- Utilize existing investment
- Perform better risk management
- Better communication
Standards
Early in 1960’s we have used the term “software architecture, but it became prevalent only in the begining of 1990’s. The first formal standard – IEEE 1471-2000 , Recommended Practice for Architecture Description of Software-Intensive Systems give people the formal definitions about software architecture area. In 2007, ISO adopted IEEE 1471-2000 ISO as ISO/IEC 42010:2007. While in 2011, IEEE 1471-2000 was superseded by ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010:2011, Systems and software engineering — Architecture description .
Architecture View
If a software system capture real world requirement, its software architecture has to be more or less complex. A single view is not sufficient to address requirements, so software architecture is commonly organized in views (multiple perspectives) especially in Large software systems. Architects describe the general information on view in software architecture, views are instances of viewpoints, examples of viewpoints are as followings:
- Use case view
- Data View
- Functional view
- logical view
- Implementation view
- Development view
- Deployment view
Some architecture frameworks or approaches gives a reference of different viewpoints collection of the system or enterprise IT, expamles are as followings
- 4+1 (UP)
- DODAF
- MODAF
- TOGAF
- Zachman framework
- Federal Enterprise Architecture
- RM-ODP
Software architectural principles
Many architecture principles have been presented in the context of Software Engineering and Object-Oriented Technologies. In software architecture perspective, it focus on the architectural meaning of those principles, It also concern the inter-dependencies among the components. However only with principles are not sufficient for building a good architectures because they provide only general guidelines. Architectural styles and architecural patterns are also important.
Architecture Styles and Architectural pattern
An Architecture style in software system is a collection of principles that can be used for system building, it usually has their focus such as data integration, networking, distributed system and etc. The Implementation of an architecture style require the software and hardware design and implementation. In maby cases, multiple Architecture styles may be used to define a concrete architecture.
A (software) Architectural pattern is a standard design in the field of Software Architecture with applying some architecture principles, but it is not equal to an architecture. An architectural pattern is a concept that solves and delineates some essential cohesive elements of a software architecture and Different architectures may implement the same pattern.
Examples of architectural styles and patterns
- Blackboard
- Client–server model (2-tier, n-tier, peer-to-peer, cloud computing all use this model)
- Database-centric architecture
- Distributed computing
- Event-driven architecture
- Front end and back end
- Implicit invocation
- Monolithic application
- Peer-to-peer
- Pipes and filters
- Plugin
- Representational State Transfer (REST)
- Rule evaluation
- Search-oriented architecture (A pure SOA implements a service for every data access point.)
- Service-oriented architecture(SOA)
- Shared nothing architecture
- Software componentry
- Space based architecture
- Structured (module-based but usually monolithic within modules)
- Three-tier model
Architecture interaction
Following Diagram show the major Architecture Interaction
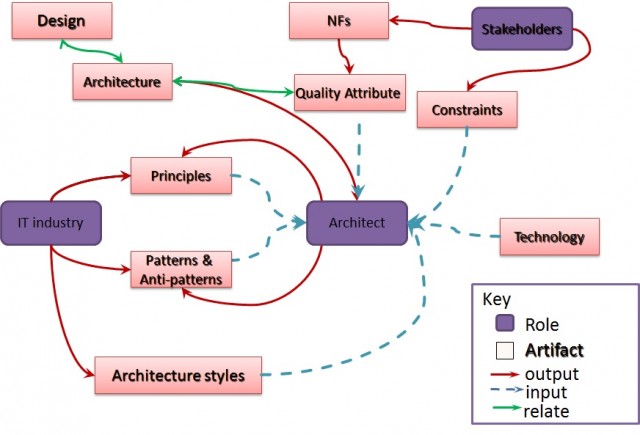
Major Deliverable of software architecture
There are three major software architecture deliverable, they are domain model, architecture blueprint and Architecture prototype.
Domain Model captures the structural and the behavioral relationships between system-level components. Architecture Description a guideline or a model that shows where components should be located and how they communicate, that also represents the deployment environment. The Description are usually in document form known as Architecture Description Document (ADD) and typically created based on UML diagrams. Finally, Architectural Prototype provides an end-to-end demonstration or implementation of the primary technologies and components, it usually act as the technologies base or proof of concept of the target software architecture. The architecture blueprint is the collection of the domain model and Architecture description Document, It facilitates communication between stakeholder.
The software architecture can be designed, analyzed, documented and implemented.
Architecture activities
There are four major disciplines related to software architecture, they are usually performed iterative and at different stages of the software development life-cycle.
Architectural analysis: It is a process to understand the requirements of the system from the stakeholder, the requirements can be divided into two main categories, the functional and non-functional requirements. Architecture focus on the non-functional requirements including the quality attributes (Quality of services), quality attribute can be divided into run-time and development time non-functional requirements, they are well-defined in ISO/IEC 25010:2011 standard.
Architecture design: As the name suggested, the architecture design is the creation of the architecture. nowadays, we are usually made use of reference architecture available in the industry to help developing own architecture. adopting technologies such as Java EE and using software framework have give us some of reference architecture.
Architecture evaluation: it is the process of determining how well of the current or under designing architecture fill the requirements or not. Architecture evaluation is an important process but often missing in software development project. Moreover, it is difficult to carry out the evaluation when the project schedule is tight. However, some of the techniques on Architecture evaluation have been developed to help the architect crop with the tasks, they include Architecture Tradeoff Analysis Method (ATAM) and TARA.
Architecture evolution: It is the process to maintain the software architecture to adopt changes.
While performing the above discipline, the Knowledge Management, Communication, decision making and documentation activities will be carried out.
System architecture and Enterprise Architecture
As I told, there are many things to learn to become an architect. There are many topics worth to be discussed here, such as architecture description languages, architecture viewpoints, architecture frameworks, architectural styles and patterns. SOA (Services Oriented Architecture) is actually one of architectural styles.
On the other hand, the system architecture and enterprise architecture are two software architecture related concepts, they have broader concerns.
Systems architecture is the architecture of systems that consists of both hardware and software. Moreover, Enterprise architecture concerns how software systems support the business process and goals of the enterprise, there are also some popular reference model of enterprise architecture such as TOGAF and Zachman Framework.
We will have further discussion on these topics, please come again if you are interested.
Peter




近期迴響